Frame alignment competencies and resources evolve to meet change head-on
With the high number of full-frame unitized vehicles on the road, automakers such as Volkswagen of America Inc. have recognized the necessity, where possible, of developing good repair methodologies without having to replace an entire frame. This has become especially important when there are restrictions about how to repair the frame, such as on heating and straightening.
The complete, safe collision repair of Volkswagen models is rooted in accessing and using the automaker’s genuine service information and employing its other approved and model-specific resources. These include service information, repair procedures, training, tools, equipment, and supplies.
Driven by the many new materials being incorporated into a vehicle’s construction mix — stronger and safer metals and alloys, innovative thermoplastics and even bonding and attachment supplies — these key resources continue to evolve. For body shops and technicians committed to Volkswagen collision repair, embracing and keeping pace with change is a must. It’s how competencies remain current over time. Even more traditional collision shop activities, such as frame straightening, have morphed, especially in recent years.

The New Mantra: Higher Strength, Lighter Weight, Improved Safety
Up until the early 1990s, mild steel (MS) accounted for nearly all of the steel used in vehicle manufacturing. It offered adequate strength and allowed for more “communized†collision repair practices because the material, associated repair knowledge, skills, procedures, and tools were similar regardless of the make and model. That is no longer the case.
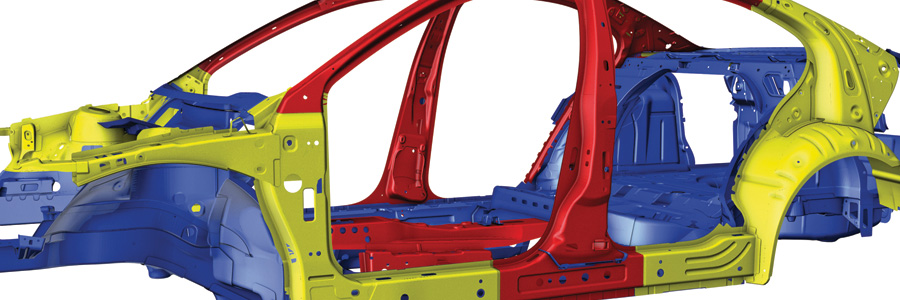
Sixty percent of the steels and alloys used in manufacturing cars today did not even exist in production vehicles 15 years ago. Technicians must be able to identify and locate where various types of steels and other materials are within a damaged vehicle because radically different repair procedures are often required by Volkswagen.
Compared to MS, the newer steel classes (listed in order of increasing strength and formability) include:
- Advanced High Strength Steels (AHSS), such as bake-hardenable and some dual-phase steels, handle more stress, provide better resistance to fatigue, improve crash energy management, and allow overall vehicle weight reduction and associated cost savings.
- Advanced High-Strength Steels and Alloys, which include more advanced Dual Phase Steels (DPS) and Transformation Induced Plasticity (TRIP) steels, provide much higher final part strength and provide higher energy absorption at a lower overall cost than both MS or AHSS parts.
- Ultra High Strength Steels and Alloys (UHSS), such as boron steel, incorporate molybdenum to create steel with benefits that only higher-priced aluminum or titanium could offer in the past, but at a lower cost.
By incorporating there stronger steels and alloys into key areas, collision energy forces are now being strategically managed and transferred away from and around passenger cabins and occupants. In addition, structural assemblies of one type of steel may be reinforced by an AHSS or UHSS, which may be hidden from view. Technicians need to know where and what they are dealing with, along with Volkswagen’s recommendations for frame straightening (heated or cold), sectioning/replacement procedures, and joining technologies.
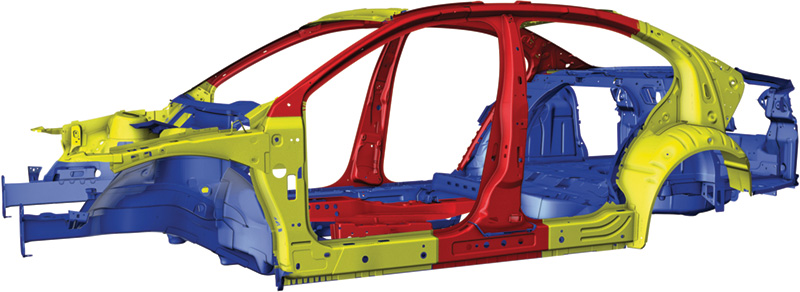
Volkswagen Empowers Collision Service-Readiness
“Maximizing survivability, not repairability, has been the primary driver in automobile design in recent years,†explains Jeffery Poole, performance training coordinator for the Inter-Industry Conference on Auto Collision Repair (I-CAR). “Increased vehicle structure complexity requires a re-evaluation of how we repair vehicles. For collision professionals to keep up, they require the right knowledge, service information, tools and equipment, ongoing training, and more.â€
Fortunately, Volkswagen provides and keeps current the resources and guidance essential to the ability of body shops to effect the complete repair of all models back to their original pre-accident safety ratings. “If a body shop follows Volkswagen standards and specifications, they can positively impact the customer experience and help maintain the vehicle resale value,†says Dan Ducharme, Volkswagen’s manager of Parts Product Management.

Examples of these resources include:
- The subscription-based Volkswagen Technical Service Information website (https://erwin.vw.com) provides independent facilities with the same service information available to the new-car dealers. Resources include model-specific collision repair information (e.g., steel schematics, repair illustrations), self-study training programs, links to online genuine Volkswagen replacement parts, approved tool/equipment vendors, and more.
- The Certified Collision Repair Facility (CCRF) program (www.vwccrf.com) administers Volkswagen certification for both dealer-affiliated and dealer-sponsored independent repair facilities. It also provides make/model/year body repair manuals, such as the 2011 Jetta manual above, that provide a useful overview for collision repair. However, the manuals may lag behind updated service information once a model is launched, so always consult the technical service information website.
- Volkswagen Collision Repair Training is required of CCRF technicians. In accordance with the automaker’s safety standards and specifications, technicians must successfully complete certain required training courses facilitated by I-CAR (www.i-car.com). VW’s list of required I-CAR courses provide training for advanced steel properties, steel unitized structural body straightening, assembly technologies, repair procedures, welding qualification tests, and more.
- Approved Vendor-Facilitated Training. CCRF-approved vendors often provide training in the use of their equipment, tools, and other products that is tailored to Volkswagen models. Check with your CCRF program contact and vendors.
Straightening is an Essential Early Step
During manufacture, Volkswagen vehicles are built using a jig and fixture system. Jigs are the key mounting points where a vehicle is attached to an automated assembly line. They are also integral features of frame alignment bench systems, should a collision repair ever be necessary. Fixtures are measuring points that are used to provide a reference for the proper location of those key mounting points throughout a collision repair. In general, fixtures are not a point that is held and pulled against. Rather, the fixture serves as a reference point for key location points to be pulled to before continuing repairs.

Using a dedicated bench system together with associated equipment and tools during collision repair, such as those supplied by Celette Inc. (which is now part of the Azimuth Group) or Car Bench, helps Volkswagen-certified collision repair facilities precisely measure, control and monitor the collision repair. The vehicle must be mounted and securely fastened to the bench at points not affected by the collision using the straightening brackets and vehicle-defined mounting points. This allows dimension variations in deformed or distorted parts to be recognized.
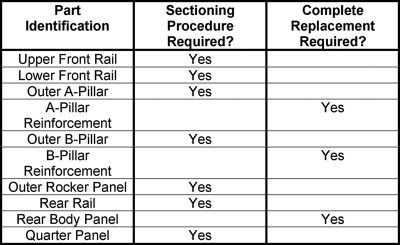
Key location mounting points can then be measured and repositioned in accordance with Volkswagen specifications and then locked down to prevent movement or damage during further repair. Whether a subframe element, suspension mounting point, safety system sensor, engine cradle, strut tower, or some other vehicle component, accurate positioning during the collision repair process is the key to replicating the original design.
For example, if bench measurement determined that these key location mounting points suffered no damage or displacement in the collision, then the vehicle can be locked down to the bench before any subsequent repair procedures are performed. If any key location point was damaged or displaced during the collision, it can be moved to the proper position on the bench, using the fixture as a reference point. Once positioned properly, the vehicle can then be locked down and further repairs initiated.
If a frame element needs to be straightened and service information indicates that it can be pulled rather than replaced, bench equipment jigs can pull the component to its proper position using fixtures as reference points to measure with. Should a part have to be sectioned or replaced, the fixtures that are located on the bench provide reference points for height, length and width that enable the repair technician to accurately place the new replacement part in its proper position relative to the rest of the vehicle.
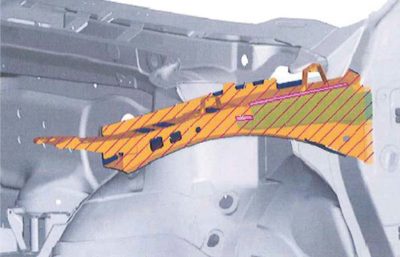
The CCRF program publishes body repair training manuals as a benefit to VW-certified body shops. While this information is relevant as an overview for collision repair, once a vehicle is launched it is quickly superseded by more current, complete and readily-available technical service repair information. Always consult the Erwin website for specific recommendations: technical bulletins, step-by-step structural measuring, straightening and joining processes, sectioning/replacement locations and directions, and more.
Never assume that straightening and repair procedures for one type of steel or other material works for all. For instance, A and B pillars can be made from a combination of MS, AHSS, and UHSS, each with different recommendations. Here are a few other considerations that collision professionals need to be aware of before starting a repair:
- Some of the hollow areas (e.g. B pillar bases, upper rails) have been filled with foam inserts to reduce the amount of noise in the passenger compartment. These must be considered to ensure identical noise characteristics post-repair.
- Required 2011 Jetta sectioning /replacement instructions reflect the construction of parts being repaired. For instance, there may be multiple locations on one part or multiple strengths of steels that require specific handling.
- For measuring and straightening the 2011 Jetta, VW has approved the MZ Plus straightening bench system (Part #VAS 6630) and associated alignment bracket set (Part #6638), both available from Celette Inc.
- Specific Tools are Required for 2011 Jetta collision repair. For example, the VW-approved tool list allows a limited number of spot welders to be used, These are equipped with computer programs that direct the proper power supply to the welding tips unique for various types of AHSSs and UHSSs. They also allow different welding arm configurations to weld hard-to-reach areas.
Resistance is Futile
The constant changes in materials used to build automobiles today poses several challenges to collision repair and in particular to those who manufacture straightening equipment. Risk management and optimizing cycle time have become entrenched necessities. On one hand, the influx of new vehicle technology has forced insurers and repair facilities to confirm repair via documentation (increasingly electronic) that provides a record of where that vehicle was before, during, and after collision repair to confirm proper realignment. On the other hand, to help improve cycle time and technician efficiency, frame and bench straightening equipment manufacturers are retooling in response to inbound materials, associated procedures, and time erosion during repair.
In the near future, vehicle realignment equipment will see a blending of current and emerging holding and pulling technologies. Some equipment manufacturers suggest that automaker-dedicated bench equipment will yield to more universal equipment that can:
- Facilitate the holding and straightening of vehicles made of old or new materials.
- Incorporate automatic electronic measurement and documentation throughout the repair process to conserve time.
- Accommodate the safe and complete repair of multiple vehicle platforms, rather than being restricted to just a single platform.
- Enable facilities to properly repair more vehicle platforms, possibly even more brands, with less variety or number of benches.
- Allow documentation to be electronic and more automatic throughout the alignment process.
Looking forward, collision shops and their technicians must continue to adapt their repair knowledge, procedures and competencies to keep pace with technological changes being made in Volkswagen vehicle structures. Some shops may find the task overwhelming, while others will see and seize this opportunity.
Either way, old collision repair paradigms are yielding to new procedures and techniques that require a thorough understanding of innovative materials, and associated equipment and methodologies. For collision facilities and technicians, relevance, survival and profitability will hinge on this.
Download PDF




0 Comments