The purpose of this article is to express what is here and now, but also what is in the future for many Volkswagen models. The same technology will, and is, being used within the Volkswagen group that includes Audi, Porsche, Bentley and Lamborghini. In Europe those same technologies can be present in Å koda and Seat models to name a few.
To understand the vehicle, one needs to know what systems and components are installed in that model. Not all models have the same equipment or behave the same way with similar equipment and combinations.
A word of caution 1. When working on this Driver Assistance equipment, and when testing and diagnosing these networks on wheels, never attempt to diagnose using scan equipment alone. A second technician must be present to read the measured values during the test.
A word of caution 2. Never rely on assistance equipment to make driving choices. It is up to the driver to make those responsible choices.
A word of caution 3. Any vehicle that displays any body or structural damage and has concerns about safety equipment must be recorded. All images and scan records must be passed to the vehicle owner/driver.
Something to think about: The average human brain reacts to stimuli in many different ways. The reaction depends on many factors such as age, sleep, drugs/alcohol and outside distractions/influences. A programmed controller(s) will react profoundly faster than human intervention.
Fact: Before the human brain reacts to a situation, the brain first has to see, recognize, assemble data then react. That reaction also means the brain has to lift that foot and slam on the brake. What just happened is in the past and the vehicle has traveled far down the road.
What should the service facility look for?
Not every option is evident in the model that is in the repair facility. There are two ways to determine what equipment and systems are installed in the vehicle. One is viewing the PR code list in the trunk or maintenance manual, and the other is a complete scan of that vehicle.
This specific example is of an Audi Q3 and very similar to the Tiguan.
Follow the scan and notice addresses 10 “Park/Steer Assist,†3C “Lane Change,†and 6C “Camera.†The gateway example identifies the installed components/equipment as the vehicle was built at the factory.
Complete Gateway Scan from the vehicle in the PR Code
01-Engine — Status: OK 0000
02-Auto Trans — Status: OK 0000
03-ABS Brakes — Status: OK 0000
04-Steering Angle — Status: OK 0000
05-Acc/Start Auth. — Status: OK 0000
08-Auto HVAC — Status: OK 0000
09-Cent. Elect. — Status: OK 0000
10-Park/Steer Assist — Status: OK 0000
15-Airbags — Status: OK 0000
16-Steering wheel — Status: OK 0000
17-Instruments — Status: OK 0000
19-CAN Gateway — Status: OK 0000
22-AWD — Status: OK 0000
25-Immobilizer — Status: OK 0000
2B-Steer. Col. Lock — Status: OK 0000
3C-Lane Change — Status: OK 0000
42-Door Elect, Driver — Status: OK 0000
44-Steering Assist — Status: OK 0000
46-Central Conv. — Status: OK 0000
47-Sound System — Status: OK 0000
52-Door Elect, Pass. — Status: OK 0000
55-Headlight Range — Status: OK 0000
56-Radio — Status: OK 0000
5F-Information Electr. — Status: OK 0000
62-Door, Rear Left — Status: OK 0000
6C-Back-up Cam. — Status: OK 0000
6D-Trunk Elect. — Status: OK 0000
72-Door, Rear Right — Status: OK 0000
Driver Assist explanations and functions:
Adaptive Cruise Control
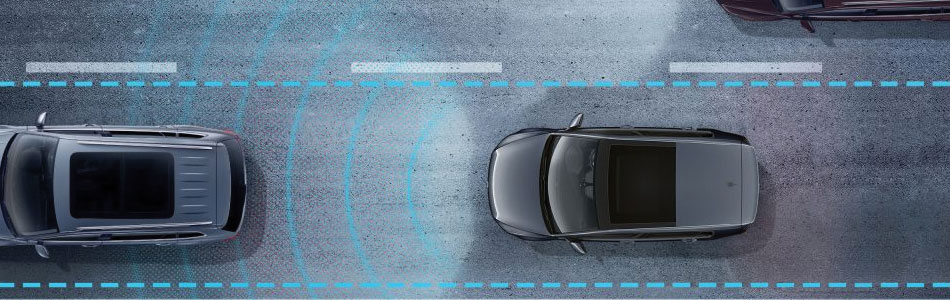
ACC, or Adaptive Cruise Control, is designed to maintain a safe distance and road speed relative to the traffic in front of the driven vehicle. Engine management and the radar controlled Front Assist traffic monitoring system will also send messages to intervene with the ABS in case of a required braking event. The driver is warned immediately.
The driver controls the speed range, acceleration, braking and distance. The driver can also restrict the speed limit. The added radar sensor immediately detects any traffic that is slowing in the radar range and reduces speed to match traffic speed. If in any event the management system detects a vehicle slowing rapidly and/or cutting into a lane, the system will first warn the driver acoustically and then perform a rapid brake nudge. If necessary, the system will stop the vehicle completely.
Included: Follow to Stop
This feature can stop the vehicle in normal traffic flow if it is necessary to prevent a collision. Applying the throttle or using the Resume control will return the vehicle to the pre-programmed speed.
Fact: In many cases and studies, the data acquired during a braking event or accident indicates that the majority of drivers insufficiently apply the brake. This is also indicated in a braking event where the driver reaction is slower.
At normal programmed highway speed, the ACC system requires no intervention and the driver can increase or decrease speeds via steering wheel controls. The steering wheel controls are connected via CAN with the ACC, radar sensors, ECM and TCM. The radar system is in constant monitoring mode when ACC is active.
Front Assist
The Front Assist system is designed to monitor road conditions/traffic speeds in front of the vehicle in conjunction with the ACC system. ACC calculates the road speed and distance of the vehicle being approached. With ACC enabled, the vehicle will decelerate to create a safe distance between each vehicle. If for some reason road traffic or environmental issues cause a potential rear-end collision, the Front Assist will intervene by issuing a driver alert and prepare the brake system for an emergency braking event. If the calculated event perceives insufficient brake pressure, Front Assist will provide the extra increase braking within the event.
The design
If the ACC and Front Assist systems sense a collision, “pre-priming†the brake system is also an aid to reducing the traveled stopping distance when the driver applies the brake. Front Assist intervention is carried out by the ABS, preventing wheel lockup and maintaining driver steering control. The radar sensor has a range of up to 650 feet with a beam angle of 12 degrees. The control unit and radar sensor are combined into a single unit.
Lane Assist
The Lane Assist system is comprised of a camera and vibrating device built into the steering wheel as a driver warning. The software for the camera is located within the rear-view mirror assembly. This system monitors the road markings and warns the driver of an unintentional deviation from within the marked driving lane. If the signal indicators are used, the system recognizes the intention and Lane Assist is disabled. If Lane Assist is enabled and the vehicle deviates, then Lane Assist sends a warning to the driver via steering wheel vibration
Note: If there are no visible markings on the road surface because of surface repairs or snow, the system will not be active.
The design
When the system is activated, Lane Assist is active at about 37 mi/hr and above. The camera begins to calculate the position of the vehicle by detecting the marked lanes. If the vehicle begins to deviate or drops below about 40 mi/hr, Lane Assist warns the driver to correct the vehicle position within the lane with a steering wheel vibration.
Activation
When Lane Assist is activated, a yellow symbol is illuminated and the camera begins to analyze the marked lanes. When the analysis is complete, the illumination switches to green, indicating that Lane Assist is active and ready.
Warnings
The system recognizes marked lane changes and if the driver’s hands are off the steering wheel. The system will warn the driver with an acoustic sound and display a warning. When the driver is back in control, the warning is disabled. The driver can also counteract the warning by steering in the correct direction.
Side Assist
When the driver intends to make a lane change, the system warns the driver when other vehicles are excessively close or within a blind spot. If another vehicle is approaching and closer than about 165 feet, a warning LED will flash in the side mirror. The system is generally designed for highway driving and can be switched off. On surface roads and general city driving, warnings can be constant. Therefore be aware that Side Assist is constantly scanning when enabled.
The design
Oncoming vehicles or stationary objects do not trigger any Side Assist warnings. Any vehicles that are one lane across the monitored lane do not trigger warnings. This system only works on speeds of about 37 mi/hr and above. The sensors have a range of approximately 200 feet. If the steering wheel is turned towards the vehicle detected, the system will intervene to avoid a collision and steers in the opposite direction (found only in combination with ‘Lane Assist’).
Note: Some models, and depending on the market, will have the warning symbol in the glass or mirror housing facing the driver.
Side note: Once again, pay attention to body damage, paint or debris on or near the sensors. During a road test for Side Assist issues, use caution and follow the rules of the road your grandfather taught you! Look over your shoulder and use all of the mirrors.
Park Assist
The Park Assist system is integrated with, and monitors, the radar sensors, electric steering rack, engine management, transmission and ABS controller systems via CAN.
The design
Enable Park Assist with the switch. Use the turn signal indicator before the vehicle passes the chosen parking space. The ultrasonic sensors in the front bumper cover will scan that open space. Park Assist will calculate if there’s enough room to maneuver the vehicle into a parallel position. When the vehicle is stopped and reverse gear is selected, Park Assist will indicate the calculated path. The driver releases the steering wheel and can view the path on the multifunctional display via rear camera. The Park Assist system begins to calculate the starting position and steers the vehicle into the chosen space. The driver has access to the throttle and brake/clutch pedals. The driver can take control and deactivate the system by steering or braking to a stop. Specifications are about 1.6 and 5 feet from the curb.
This system can allow the vehicle (if it fits) to maneuver into that chosen space multiple times by controlling the vehicle with the throttle and brake/clutch pedals. Again, take control by holding the steering wheel or stop the vehicle completely.
Side note: Do these vehicle owners actually get a pass on a driving test?
Park Distance Control (PDC)
The Park Distance Control uses ultrasonic sensors that warn the vehicle operator of objects in its path. Depending on the system and with a rearview camera, the driver can see objects in reverse and hear the warnings. The closer the object detected, the faster the warnings sound. With the multimedia interface, the driver can also use the grid lines on the display to accurately maneuver the vehicle into position.
Other systems also incorporate PDC in the front bumper cover and with close proximity to front objects, the driver is warned audibly.
Post-Collision
Quite a bit of research has been compiled after a collision and, of course, one factor comes into play.
Newton’s first law of motion: “An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.â€
Not all collisions are the same. There are multiple/complex factors to consider but the Post-Collision system can mitigate more potential damage or injuries.
The design
The air bag controller and the sensors attached to the vehicle are constantly recording data. That data will come from the ECM, TCM, ABS and the sensors attached to the air bag controller.
At the moment of impact, the air bag controller will record the event and the Post-Collision system is informed via CAN messages. The system will initiate the ABS system until the vehicle decelerates to about 6 mi/hr.
At the moment of impact, the brakes will be applied immediately and as long as necessary, to slow the vehicle and help prevent other damage or injuries. During the Post-Collision event, the driver can still maneuver the vehicle as necessary using the steering control, brakes or throttle back to a safe path.
Rearview Camera
The rearview camera is connected via sensors and the multimedia display to aid the driver when in the reverse direction. Via CAN and also with Park Assist the camera is enabled with the Park Assist switch.
The design
A common feature with the camera system is also the acoustic warnings with the PDC system. The multimedia interface incorporates grid lines in the display to align the vehicle or help indicate objects while the camera is enabled. The display will also indicate the direction the vehicle will travel via steering angle sensor.
Along with the rearview camera and multimedia device, options such as navigation can be added when the vehicle has that option enabled and/or installed.
Rear Traffic Alert
The rear traffic alert is a system that uses radar sensors to warn the driver when a vehicle approaches (especially in a blind spot), sounding an audible alarm. The range is approximately 165 feet on both sides.
The design
When the system is active, sensors at the rear bumper monitor the lateral area behind the vehicle. The sensors sweep a wide area (about 180 degrees) to inform the driver of any obstacles in its path. If the driver does not take action and an impending collision is calculated, the ABS intervenes and applies the brakes. Warning messages are also sent to the driver information center and/or multimedia interface.
Something to think about
The modern body shop will be horrified when they find out what the costs will be for replacement and adaptations for these intelligent and complicated systems. Work with the reputable body shops and explain to the vehicle owner the complexities and adaptations of Driver Assist systems.
Driver distraction is now the leading cause of accidents, just above drunk driving.
Intelligent Crash Response System (ICRS)
In the event of a collision that deploys the air bags, the ICRS can turn off the fuel pump, unlock the doors and activate the hazard lights. That will mean that the engine will stall but critical electrical systems will remain active.
Dynamic Light Assist
The system relies on sensors and lighting control that offer the driver automatic assistance when approaching another vehicle when the normal lights (low beams) are active.
The design
If the vehicle has cornering lights added as an option, the beams will move slightly to the right. The camera in the rearview mirror monitors the incoming light and relays the message to the Dynamic Light Assist system, controlling the dynamic headlamp motors.
Light Assist
Another improvement for driver control is the Light (high beam) Assist system. The system also uses the camera built into the rearview mirror.
The design
The system is activated above about 37 mi/hr automatically when the driver selects the low beam switch position. With the built in camera, the incoming light messages the controller to switch the high beam to low beam when detecting oncoming traffic if the high beam switch is in the On position. Light Assist control monitors the camera, road speed and the Hi/Low switch position.
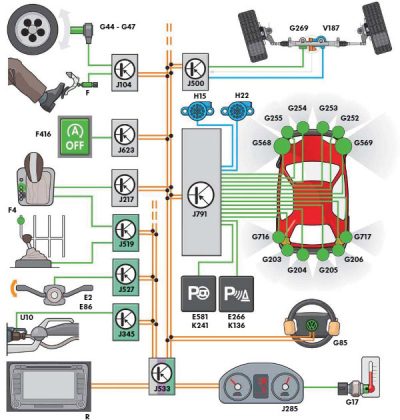
This included image is in relation to Park Assist only. It gives a very clear idea of the Park Assist complexity. If for any reason tests are to be performed on any Driver Assist systems, familiarize yourself and your staff by reading the operators manual first! Understand how these systems operate, how to enable and disable the systems. Ultrasonic and radar sensors require adjustments and adaptations after replacement.
Remember: Search for all available TSBs and Dealer Campaigns associated with the vehicle if repairs or adjustments are required.
If programming updates are required, do them as well.
Any adjustments or replacement of chassis, suspension, and suspension control components will require alignment and control module adaptations.
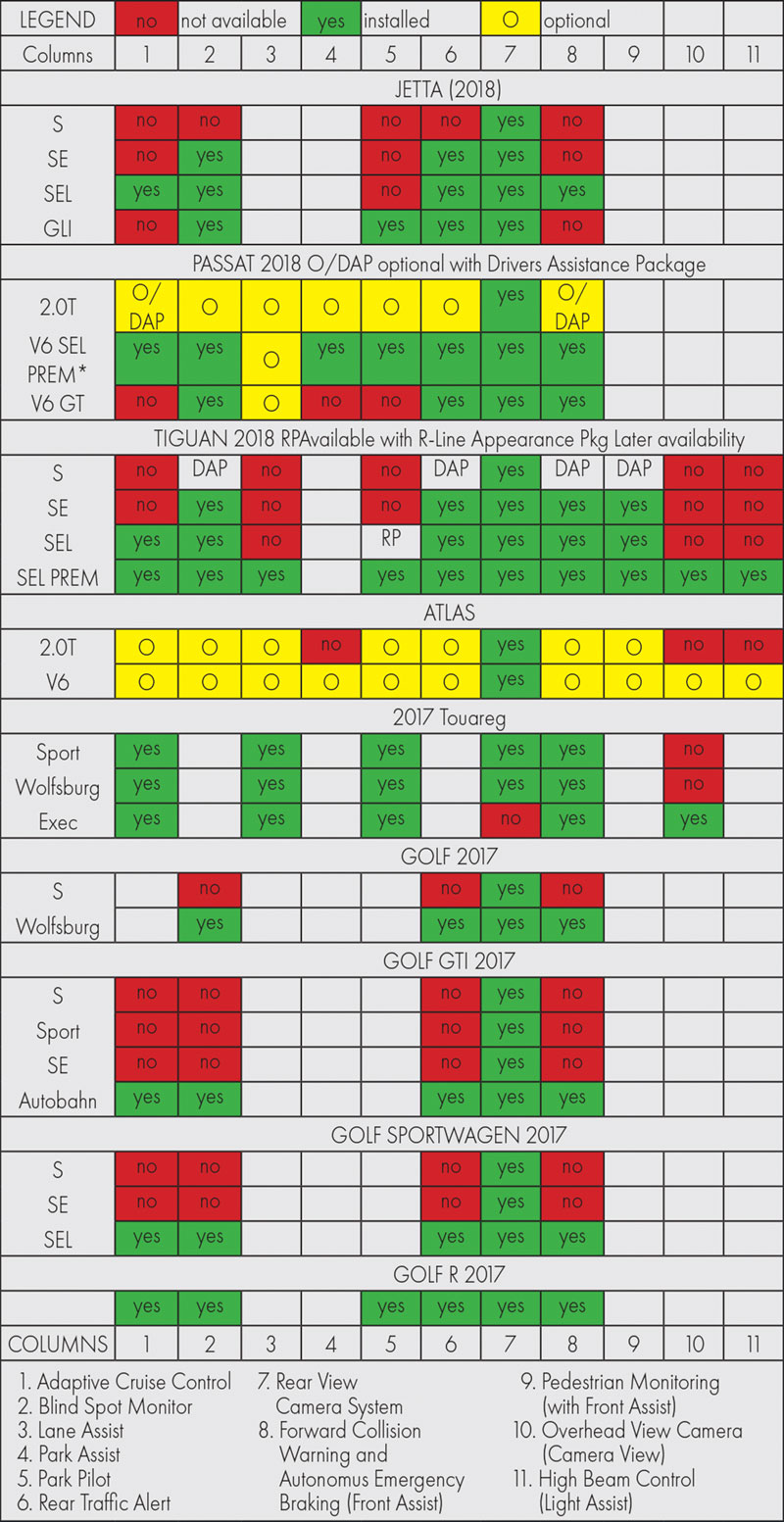
To date, the chart below indicates the modern vehicles that do or don’t have some or all Driver Assist options.
Download PDF


















0 Comments